Significance Of Biodiversity
Biodiversity, or biological diversity, encompasses the variety of all life forms on Earth, including plants, animals, microorganisms, and the ecosystems they form. The significance of biodiversity is vast and multifaceted, impacting ecological, economic, social, and cultural aspects of human life and the environment.
1. Ecological Significance
Ecosystem Stability and Resilience:
- Functionality: Biodiversity ensures the stability and functioning of ecosystems by promoting processes like nutrient cycling, pollination, decomposition, and climate regulation. Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to disturbances, such as climate change, natural disasters, and human activities .
- Interactions: Different species interact in ways that enhance ecosystem productivity and resilience. For instance, diverse plant species can improve soil health and water retention, leading to more robust and stable ecosystems .
Habitat Provision:
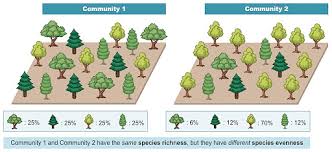
- Niches: Biodiversity provides a range of habitats and niches that support various forms of life. This diversity of habitats is crucial for the survival of many species, particularly those that are specialized and cannot adapt to different environments .
2. Economic Significance
Resource Supply:
- Agriculture: Biodiversity underpins agriculture by providing a variety of crops, livestock, and genetic resources that can enhance food security and resilience to pests and diseases. Genetic diversity in crops is vital for developing new varieties that can withstand environmental stresses .
- Medicine: Many pharmaceuticals are derived from plants, animals, and microorganisms. Biodiversity serves as a reservoir of potential medicines and therapeutic compounds, with many undiscovered species potentially holding cures for diseases.
Ecosystem Services:
- Pollination: Biodiversity is critical for pollination, which is essential for the production of many crops and wild plants. Pollinators like bees, birds, and bats contribute significantly to global food production and ecosystem health .
- Climate Regulation: Forests, wetlands, and oceans play crucial roles in sequestering carbon and regulating the Earth’s climate. The diverse species within these ecosystems contribute to their effectiveness in mitigating climate change .
3. Social and Cultural Significance
Cultural Identity:
- Traditions and Knowledge: Many cultures have deep-rooted connections with their natural environment, with biodiversity playing a central role in traditions, folklore, and traditional knowledge. Indigenous communities, in particular, rely on biodiversity for their cultural identity and survival .
- Recreation and Tourism: Biodiversity-rich areas attract tourists, providing economic benefits through ecotourism. National parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and marine reserves offer recreational opportunities that enhance human well-being and generate income for local communities .
Health and Well-being:
- Mental Health: Natural environments and biodiversity contribute to mental health and well-being by providing spaces for recreation, relaxation, and inspiration. Exposure to nature has been shown to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression .
4. Conservation and Ethical Significance
Intrinsic Value:
- Moral Responsibility: Many people believe that all species have an intrinsic right to exist, independent of their utility to humans. This ethical perspective drives conservation efforts aimed at protecting all forms of life .
- Future Generations: Biodiversity conservation is essential for ensuring that future generations inherit a planet rich in life and ecological services. Protecting biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the natural heritage and ecological wealth of our planet .
Conclusion
Biodiversity is fundamental to the health of the planet and human well-being. It supports ecosystem stability and resilience, provides essential resources, contributes to cultural identity and mental health, and has intrinsic ethical value. Preserving biodiversity through conservation efforts is vital for sustaining life on Earth and ensuring a balanced and functional environment for future generations.
Also Read