Ecological Sensitive Zones Explained
Ecological Sensitive Zones (ESZs), also known as Ecologically Fragile Areas (EFAs), are areas notified by the government of a country that are crucial for the sustenance of ecological balance. These zones are typically around protected areas such as national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves. Here are some key points about ESZs:
Purpose
- Biodiversity Conservation: Protect biodiversity and ensure the survival of endangered species.
- Environmental Sustainability: Maintain ecological balance by regulating development activities.
- Buffer Zones: Act as buffer zones to reduce the impact of human activities on protected areas.
Criteria for Identification
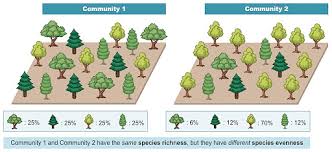
- Species Richness: Areas with high species diversity and endemism.
- Fragile Ecosystems: Regions with ecosystems that are sensitive to disturbances.
- Conservation Value: Areas that are vital for the conservation of various flora and fauna.
Regulatory Framework
- Prohibited Activities: Mining, industrial operations, major hydroelectric projects, and other activities that can cause significant environmental harm.
- Regulated Activities: Sustainable agriculture, horticulture, and minor construction are allowed under strict guidelines.
- Permitted Activities: Non-disruptive, eco-friendly activities such as organic farming, use of renewable energy sources, and eco-tourism.
Implementation
- Government Role: National and state governments collaborate to notify and manage ESZs.
- Community Involvement: Local communities and stakeholders are often involved in the planning and conservation efforts.
Challenges
- Development Pressures: Balancing development needs and conservation can be challenging.
- Enforcement: Ensuring compliance with regulations requires effective monitoring and enforcement mechanisms.
- Awareness: Increasing public awareness about the importance of ESZs is crucial for their protection.
Global Examples
- Western Ghats (India): A biodiversity hotspot with numerous ESZs.
- Great Barrier Reef (Australia): Protected to prevent damage from human activities.
- Amazon Rainforest (South America): Large areas are designated as protected zones to preserve biodiversity.
Benefits
- Environmental Protection: Helps in the preservation of critical habitats and ecosystems.
- Sustainable Development: Promotes eco-friendly development practices.
- Climate Regulation: Plays a role in carbon sequestration and regulating local climates.
Questions For Practice
Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the primary purpose of establishing Ecological Sensitive Zones (ESZs)?
- A. To promote urban development
- B. To protect and conserve biodiversity
- C. To increase industrial activities
- D. To expand agricultural land
- Which of the following activities is typically regulated in an ESZ?
- A. Sustainable agriculture
- B. Large-scale mining
- C. Major hydroelectric projects
- D. Industrial operations
- What is usually the criteria for identifying an ESZ?
- A. High population density
- B. High species richness and endemism
- C. Proximity to urban areas
- D. Presence of major roads
- Who is generally involved in the management and conservation of ESZs?
- A. Only government officials
- B. Only local communities
- C. Both government officials and local communities
- D. Only international organizations
- Which of the following is a common challenge faced in managing ESZs?
- A. Excessive wildlife population
- B. Lack of natural resources
- C. Balancing development needs with conservation
- D. Overabundance of protected areas
True or False
- ESZs are areas where industrial and mining activities are completely banned. (True/False)
- Local communities are often excluded from decision-making processes related to ESZs. (True/False)
- The Western Ghats in India is an example of a region with numerous ESZs. (True/False)
- Enforcement of ESZ regulations is usually straightforward and without challenges. (True/False)
- Eco-tourism is typically encouraged in ESZs as long as it follows strict guidelines. (True/False)
Short Answer
- Explain why buffer zones around protected areas are important.
- What are some examples of activities that might be permitted in an ESZ?
- Discuss a common challenge faced in the enforcement of ESZ regulations.
- Describe the role of local communities in the management of ESZs.
- How do ESZs contribute to climate regulation?
Also Read